Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration
Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Uniform Acceleration in 2D Motion, Trajectory of a Particle in 2D Motion & Equation of Trajectory in 2D Motion etc.
Important Questions on Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration
The trajectory of a projectile in a vertical plane is where are constants, and and are respectively the horizontal and vertical distances of the projectile from the point of projection. Find the maximum height attained by the projectile and the angle of projection from the horizontal.
Motion of an aeroplane is an example of _____ dimensional motion.
An object moves with constant acceleration . Which of the following expressions are also constant.
A fighter plane is flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed 720 km/h. At what angle of sight (w.r.t. horizontal) when the target is seen, should the pilot drop the bomb in order to attack the target ?
(Answer in degrees correct to two decimal places)
Cotyledons are also called-
The equations of motion of a projectile are given by and . The angle of projection is –
In a vertical disc two grooves are made as shown in figure. AB is a diameter. Two balls are dropped at A one in each groove, simultaneously. Then :
A body moves with uniform acceleration then which of the following graph is correct?
The equation of projectile is . The angle of projection and initial velocity is -
A particle is moving in -plane with a constant speed such that its displacement is given by where is component of velocity along -axis. displacement of the particle when slope of tangent on its path is is
A bead of mass is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical and vertex at the origin as shown in figure and whose equation is . The wire frame is fixed and the bead can slide on it without friction. The bead is released from the point on the wire frame from rest. The tangential acceleration of the bead when it reaches the position given by is :
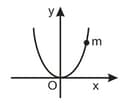
A particle has initial velocity and has acceleration Its speed after is
The x and y co-ordinates of a particle are and . Then the motion of the particle is
A particle is moving in plane with and . The displacement versus time graph of the particle would be
A rigid rod leans against a vertical wall (axis) as shown in the diagram. The other end of the rod is on the horizontal floor. Point is pushed downwards with constant velocity. Path of the centre of the rod is
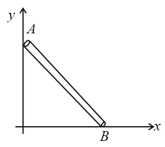
In projectile motion, the modulus of rate of change of speed
A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola (y-axis vertical) with a bead of mass on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the x-axis with a constant acceleration . The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the y-axis is -
A particle of mass moves along a curve . When particle has x-coordinate as and component of velocity as then :
